When information sharing can concretely help our companies to anticipate cyber attacks.
It’s always a pleasure to feature insightful guest contributions here on CyberSec Café. Today, I bring you an article that dives into the transformative power of collaboration in cybersecurity.
This piece explores the Threat Intelligence Sharing Project, an initiative that exemplifies how collective efforts and innovative platforms— like Malware Information Sharing Platform (MISP) —can redefine the way we tackle cyber threats. I’m thrilled to share this with our readers, as it highlights practical approaches to making our digital world safer.

Introduction to the Threat Intelligence Sharing Project
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is a top priority for all businesses, large and small. Increasing cyberattack attempts require sophisticated tools and collaborative strategies to ensure the protection of sensitive data and corporate infrastructure. In this context, in 2024 several CISOs decided to join forces and develop a project called “Threat Intelligence Sharing”; an initiative to optimize the rapid and efficient sharing of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs), to materialize a common vision of collaboration.
Objectives of the Threat Intelligence Sharing project
The main objective of the Threat Intelligence Sharing project is to share, in the shortest possible time, the Impairment Indices defined as Gold. These IOCs, identified as particularly relevant and critical, are collected by the various companies participating in the project, through their security systems. Timely implementation of these IOCs in a preventative mode can help all companies involved stop attack attempts before they can cause damage.
What Are Gold IOCs?
Gold IOCs are compromise identifiers that have passed a rigorous validation process and have been classified as highly reliable.
Transforming a Compromise Indicator (IoC) into a Golden IoC requires several key steps:
- IoC identification
- Collection of all available data
- In-depth analysis
- Assessment of severity and assignment of Golden IoC status.
These steps ensure the accuracy, reliability, and relevance of the indicator for sharing.
These indexes include information about malicious IP addresses, malicious file hashes, phishing URLs, and other characteristics that can be used to detect and prevent cyber threats. Sharing these Gold IOCs allows companies to obtain a high level of protection, based on verified and up-to-date data.
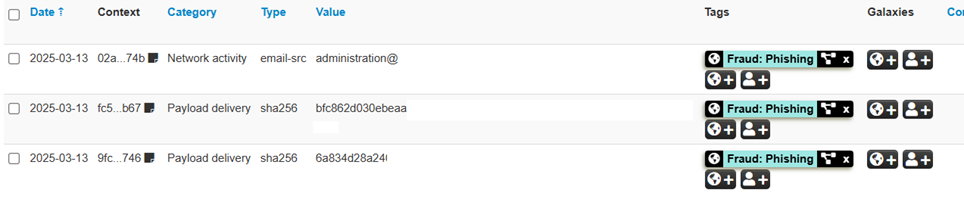
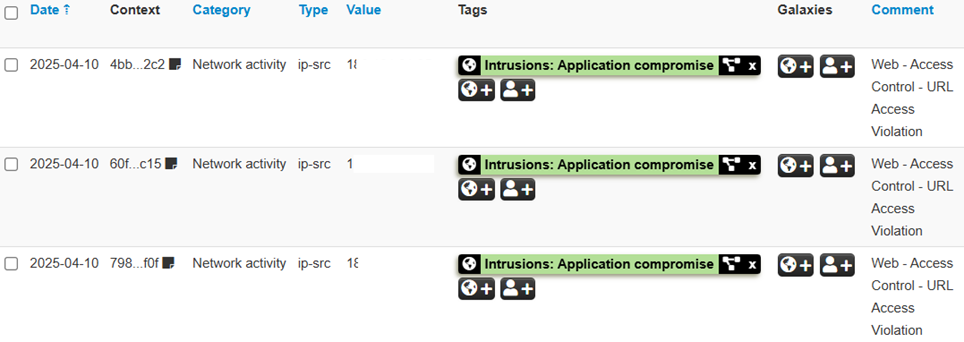
How MISP Powers Collaboration
The strength of the Threat Intelligence Sharing project lies in the collaboration between the participating companies. Each company contributes its own observations and analysis of security systems, creating a shared database of IOC Gold. This database is accessible to all the entities involved in the project, which can use it to improve their defenses. Collaboration allows you to have a more complete and up-to-date view of threats, facilitating the prevention and response to attacks.
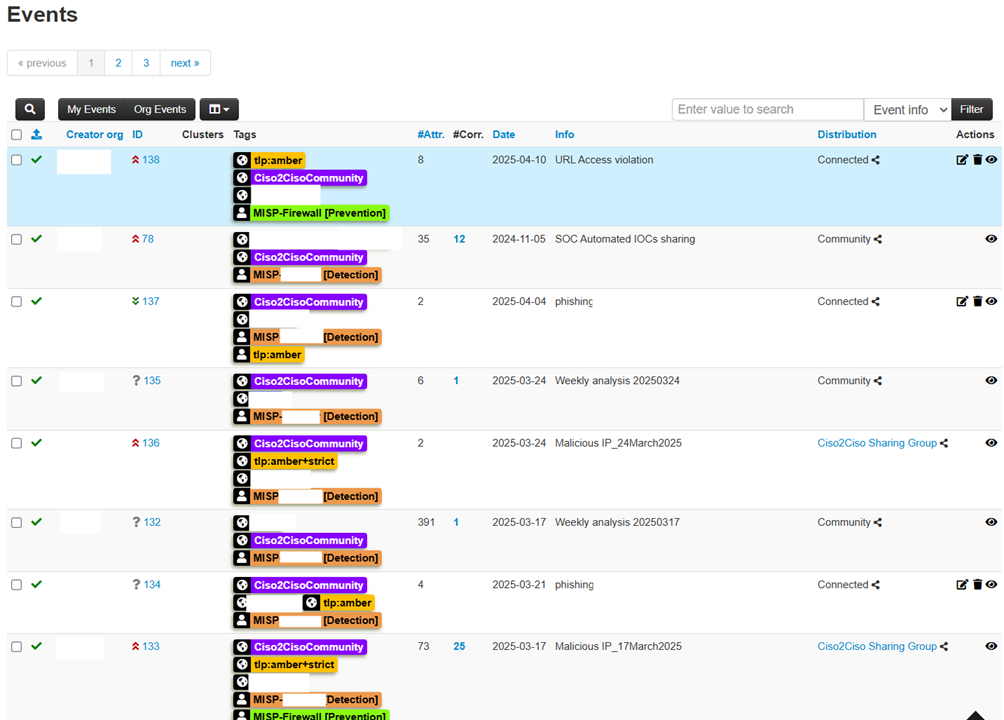
Implementation and benefits
How to share
Gold IOCs are shared through the Malware Information Sharing Platform (MISP), an open-source platform that facilitates the exchange of threat information between different entities. MISP allows you to automate the sharing process, ensuring that IOCs are deployed quickly and securely. Companies can configure MISPs to receive real-time updates, immediately integrating them into their defense systems.
Benefits of implementation
Implementing Gold IOCs in preemptive mode offers several benefits:
- Proactive protection: The ability to block attack attempts before they can compromise business systems.
- Constant updates: Gold IOCs are continuously updated, ensuring that defenses are always based on current information.
- Reduce risk: Sharing information allows you to identify and mitigate emerging threats in a timely manner.
- Resource efficiency: Using validated IOCs reduces the time and resources required for investigation and incident response.
The crucial advantage of having validated Threat Intelligence information through the Threat Intelligence Sharing project is its ability to enhance risk mitigation against targeted cyber threats across industries and regions. Unlike using IOCs from open or paid intelligence sources, which can provide millions of indicators of compromise, but often not relevant to the business context, the information shared in the Threat Intelligence Sharing project is highly selective and relevant. These Gold IOCs are validated and contextualized, ensuring that companies receive accurate and relevant data to the real threats they face. This targeted approach reduces noise and false positives, allowing companies to focus their resources on preventing and responding to attacks that have a high impact in their specific context, thus improving the efficiency and effectiveness of their cyber defenses.
Conclusions
The “Threat Intelligence Sharing” project represents a fundamental step in the collaborative protection of corporate infrastructures. Sharing Gold Impairment Ratios allows you to achieve a proactive and efficient defense, based on verified and up-to-date data. The collaboration between the participating companies, facilitated by the MISP platform, guarantees a rapid and coordinated response to cyber threats, improving the overall security of all the entities involved. In an increasingly interconnected and vulnerable world, initiatives such as Threat Intelligence Sharing are essential for protecting corporate data and infrastructure, ensuring a more secure digital future.



Recent Comments